Resource Efficiency: Don’t waste the future
Impacted SDGs
Key megatrends
Resource scarcity
Population growth
Energy transition & climate change
We are facing an existential environmental crisis…
Climate action failure
0.5 - 0.7 bn People living in areas under water by 2100 without further action
Natural resource crisis
3 million km² of tropical forest (size of India) lost by 2050
Biodiversity loss
28% of animal species at risk of extinction in the next 50 years
Resource efficiency sees opportunities across most of human activity…
Live
1 Circularity & waste
Move
2 Green mobility
Eat
3 Healthy low-carbon diets
Produce
4 Sustainable industry
Plug-in
5 Net zero energy
- Waste management
- Recycling of materials
- Circular products
- Sustainable packaging
- Water treatment
- Alternative biomass use
- Electrification power of power trains
- Low carbon shipping and aviation
- Next-gen batteries and fuel cells
- Energy infrastructure and services
- Shared mobility
- Aquaculture
- New farming methods
- Crop preservation
- Food waste reduction
- Sustainable and healthy foods
- Green materials
- Energy efficiency
- Sustainable buildings
- Carbon capture,
utilisation and storage - Natural capital & offsets
- Renewables
- Hydrogen / green fuels
- Distributed energy
- Waste-to-energy
- Energy storage
- Smart grid
Source. World Economic Forum Global Risks Report 2021; UN Global Resources Outlook 2019; WEF Nature Risk Rising 2020; University of Arizona; Munia et. al -Future Transboundary Water Stress and Its Drivers Under Climate Change: A Global Study (2020); WWF; Engelmann & Busch -The Future of Forests: Emissions from Tropical Deforestation with and without a Carbon Price, 2016–2050
Exit case: Sortera
Investment snapshot
- Summa signed an agreement to sell Sortera to Nordic Capital in March, deal closed in April 2021
- Topline growth five folded during ownership period through organic growth and M&A
- Two new divisions added: Materials and Industry1
- Geographical expansion to Finland and expansion to cover 75% of the Swedish market
SDG value creation impact
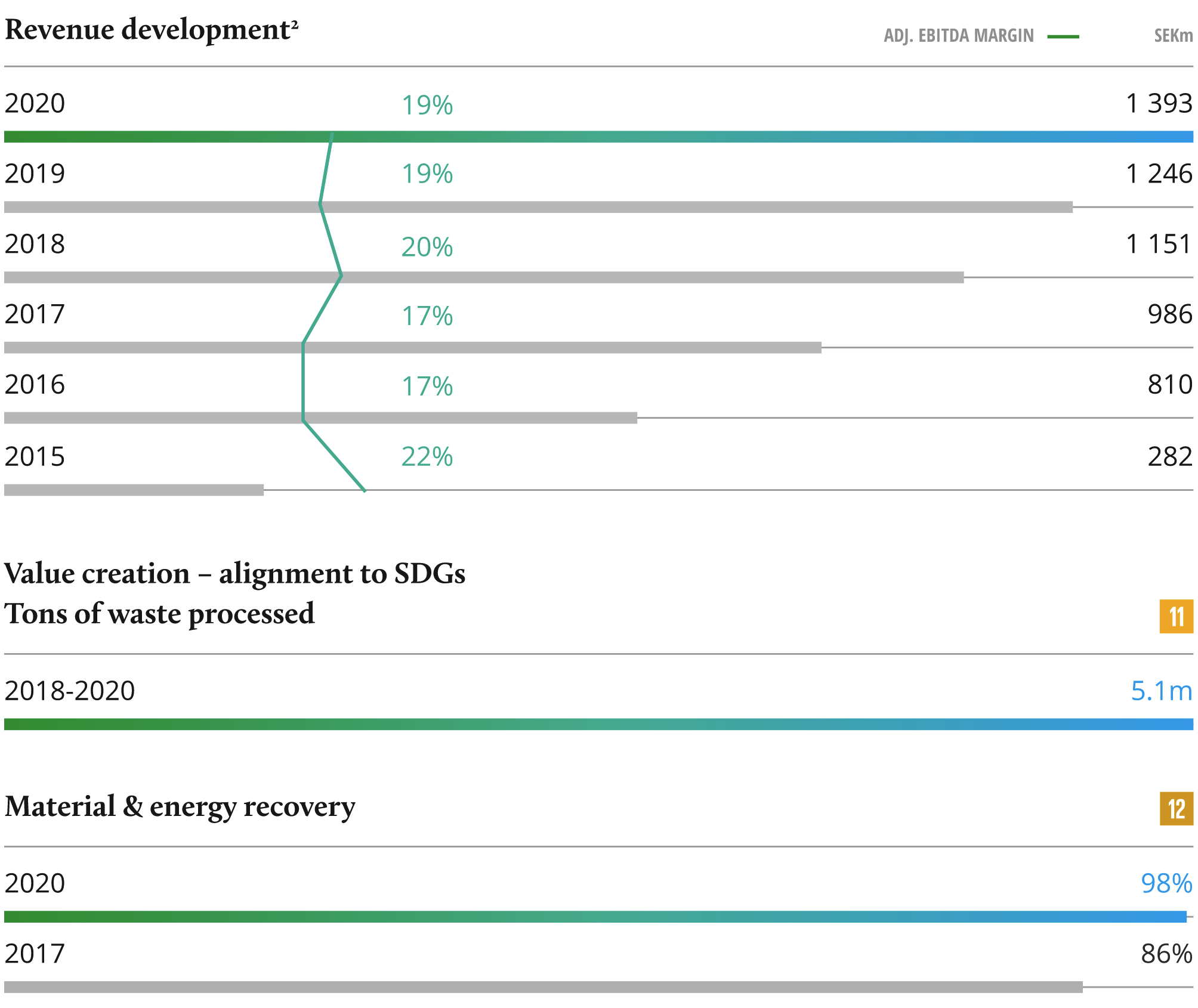
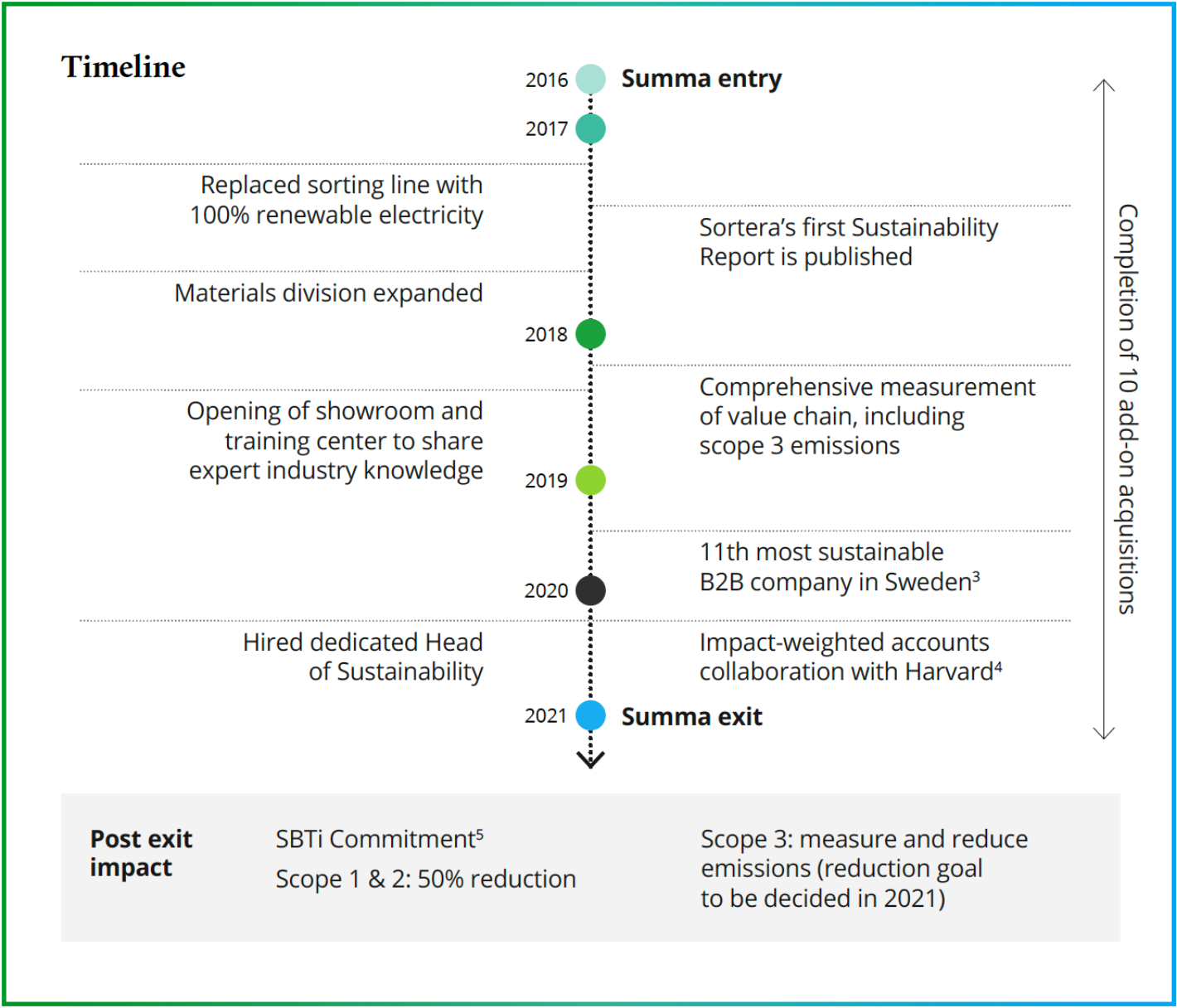
Exactly five years after acquiring Sortera, Summa signed an agreement to sell Sortera to Nordic Capital. Throughout the ownership period, the company has displayed an impressive growth story with active value creation through add-ons, organizational improvements, and a focus on sustainability.
Since entry, Sortera has grown from 95 employees in 2016 to 400+ in 2021 and achieved +89% Adj. EBITDA growth2, 2016A-2020A. Despite the recent pandemic, Sortera saw a revenue increase of 12% in 2020, demonstrating a very resilient business model.
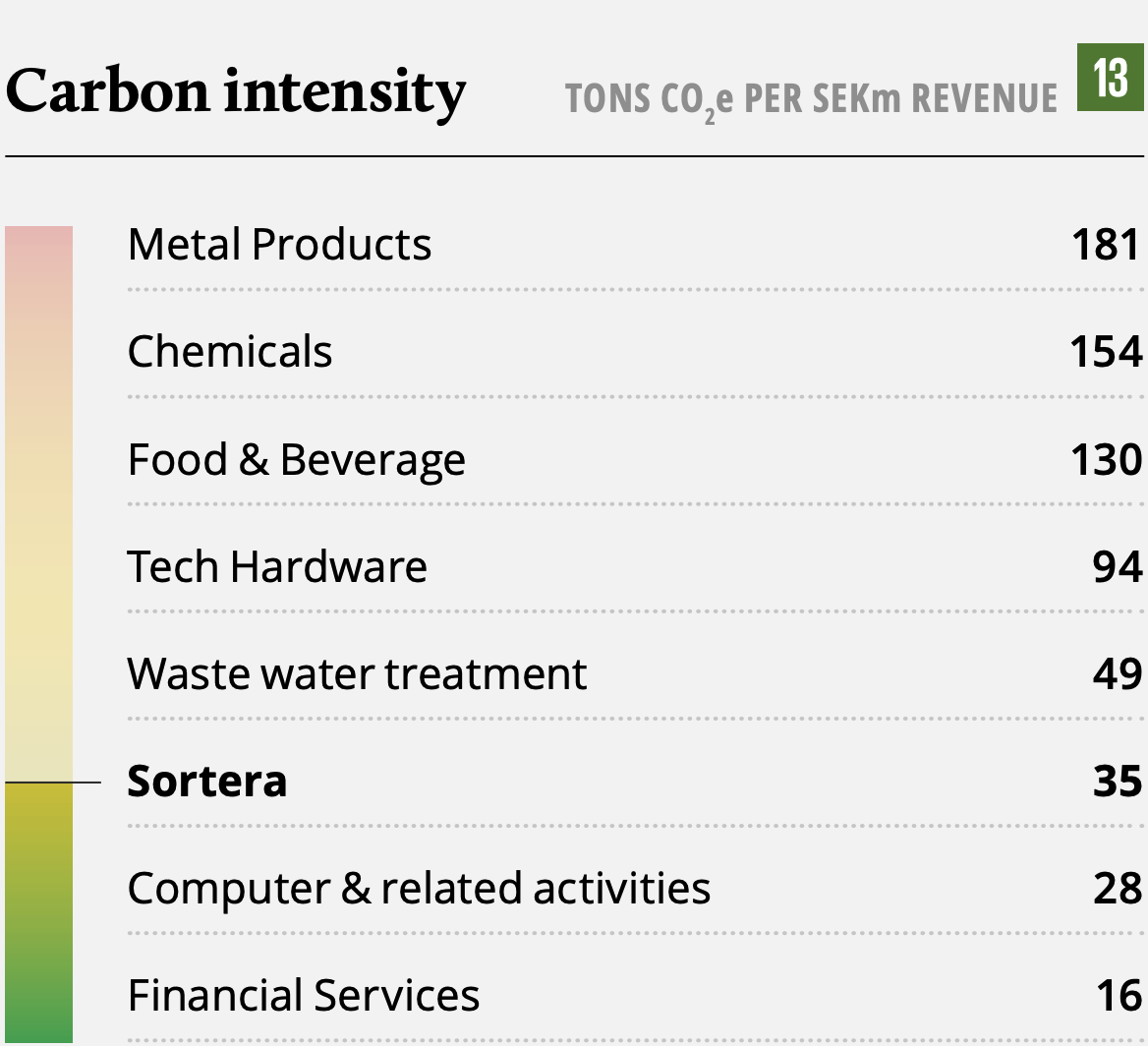
The SDGs are firmly rooted within Sortera’s business model, and they are continuously developing their approach to ESG matters. Sortera has increased its positive impact on society as the recycling rate and their ability to handle more waste have evolved. Although recycling, material waste management, and industrial waste services naturally generate emissions, the processes also provide significant emission avoidance.
- Sortera’s core business lines and product offerings include Recycling of construction and industrial waste, Materials (purchasing, selling, and trading waste), and industry (high pressure services within rinse, industrial cleaning, asbestos removal, and vacuum blowing)
- Pro-forma adj. from 2016
- Sustainable Brand Index: https://www.sb-index.com/sweden-b2b#sb_index_SE_download_official_report_2019_b2b
- The Project is part of a broader Impact-Weighted Accounts Initiative (IWAI), which is a research-led joint effort by the Global Steering Group (GSG) and the Impact Management Project (IMP). https://www.hbs.edu/impact-weighted-accounts/Pages/default.aspx
- SBTi: Science Based Targets Initiative: https://sciencebasedtargets.org/
- Sortera’s core business lines and product offerings include Recycling of construction and industrial waste, Materials (purchasing, selling, and trading waste), and industry (high pressure services within rinse, industrial cleaning, asbestos removal, and vacuum blowing)
- Pro-forma adj. from 2016
- Sustainable Brand Index: https://www.sb-index.com/sweden-b2b#sb_index_SE_download_official_report_2019_b2b
- The Project is part of a broader Impact-Weighted Accounts Initiative (IWAI), which is a research-led joint effort by the Global Steering Group (GSG) and the Impact Management Project (IMP). https://www.hbs.edu/impact-weighted-accounts/Pages/default.aspx
- SBTi: Science Based Targets Initiative: https://sciencebasedtargets.org/
Sortera - turning waste into resources
SDG alignment
-
Total
19% -
Management
11% -
Board
50%
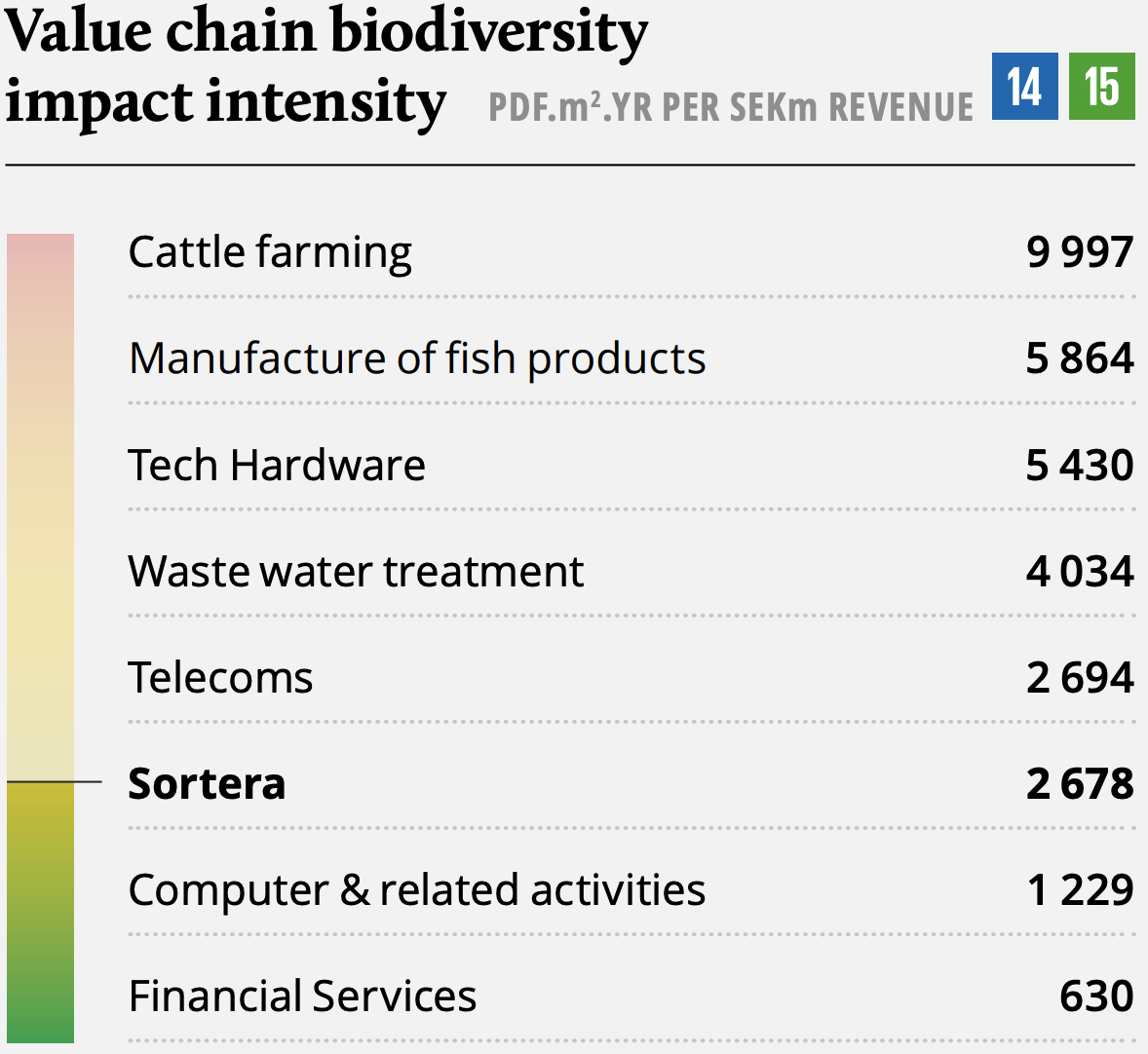
Sortera at a glance
Sortera is a complete environmental services provider and one of the leading niche providers of construction and industrial waste solutions in the Nordics. The company is divided into three business areas: Recycling (construction recycling services), Industry (Industrial cleaning, excavation, pressure washing etc.) and Materials (handling of heavy masses and water treatment).
Sortera is currently active across Sweden and Finland, with sites in Stockholm, Gothenburg, Malmö and Helsinki. The company also operates under the brands BIG BAG, Åkerisäcken, Vaihtolavacom, EnvyTech and MTIB.
Key developments in 2020
During 2020, group revenues grew by 12% vs. 2019, with growth across all divisions and limited impact of Covid-19. Sortera also closed two add- on acquisitions in 2020: Vaihtolavacom and W.A.C. Recycling. Vaihtolavacom is a Helsinki based construction recycling services company and was Sortera’s first acquisition outside of Sweden. W.A.C Recycling, handles industrial waste in southern Sweden, further strengthening the Materials Division.
In Q1 2020, the Deputy CEO took over the role as CEO, while the former CEO transitioned into the role as senior advisor to the firm and remained asmember of the Board.
New sustainability reporting standards and systems have also been implemented during the year, in addition to the recruitment of a Head of Sustainability.
- Backfilling, Energy Recovery and Material Recycling
- Estimated by Normative, based on data on the
tonnage of the various waste categories handled.
Impact dimensions
The challenges we face
While resource scarcity is a growing challenge and GHG emissions are rising globally, the European construction sector generates ~30% of all European waste, requires substantial raw material extraction and causes high GHG emissions.1 As a result, the European Commission has implemented measures to increase industry recycling levels, meaning that construction firms must take action now to meet the new requirements.
ESG goals
Sortera has worked to track and improve ESG targets since they published their first Sustainability Report in 2017. At that time, they defined a long-term goal for 100% of their handled waste to be recycled or reused. 4 years later they have nearly reached their goal as 98% of the waste is recovered. They have aligned their ESG goals with the UN SDGs, which include targets to increase diversity in their organization and to increase their positive impact on the environment.
- A new circular economy action plan, European
Commission, Brussels 11.03.2020 Available at:
https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legalcontent/EN/
TXT/?qid=1583933814386&uri=COM:2020:98:FIN - https://www.scb.se/contentassets/9eb07fe802b74ac98b71f8c7ab5a3d92/
mi0305_2018a01_br_misambr2001.pdf - EU Construction & Demolition Waste
Management Protocol, September 2016 - EPA, 2018. Available at: https://www.epa.gov/energy/greenhouse-gas-equivalencies-calculator
Kiona - Putting an end to wasted residential energy

SDG alignment

-
Total
14% -
Management
16% -
Board
20%


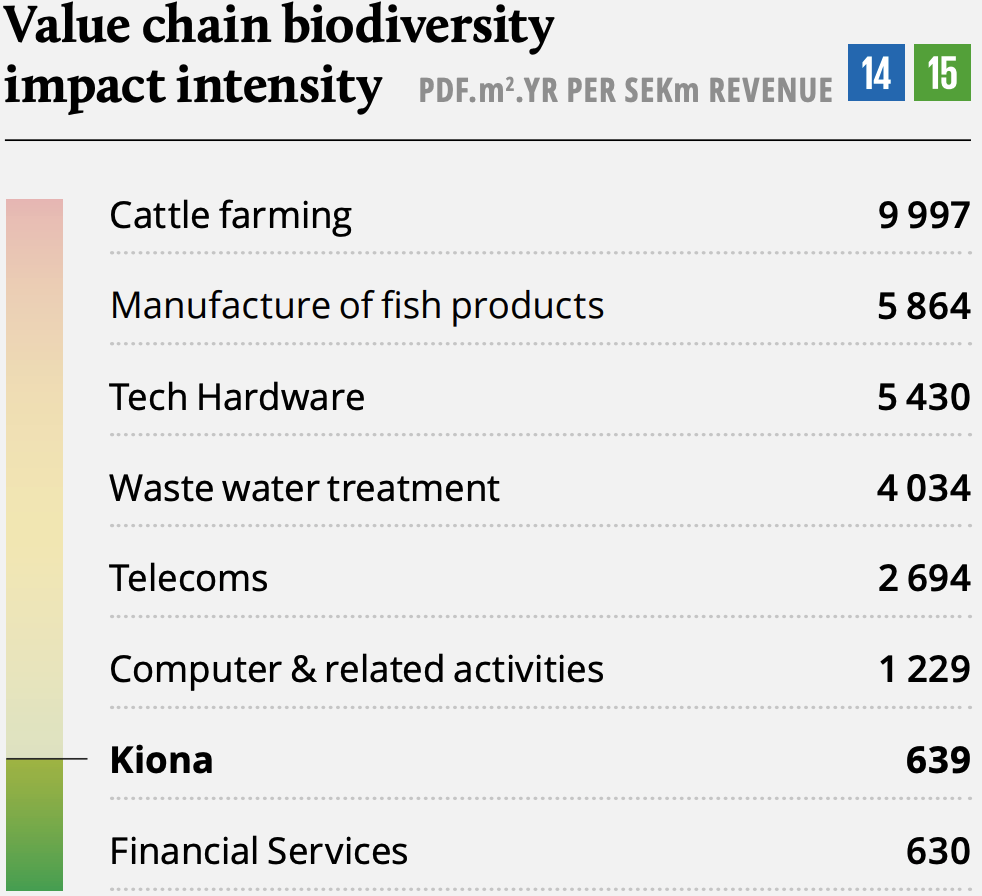
Kiona at a glance
Kiona is the leading platform in the market for smart energy solutions. The group was formed in 2021 as a result of the merger between IWMAC (2001), Egain (2003) and Cebyc (2002) - with multiple ongoing acquisitions contemplated.
The key segments are retail & industrial refrigeration, multi-residential buildings, and public & commercial buildings. The merged group also provides several ancillary software services to their customers, such as communication, analysis, and intelligence.
Kiona is market-leading in their core segment. They have an unparalleled contractor network in Scandinavia with 90 partners in Norway and Sweden.
Key developments in 2020
The initial pro-forma figures of IWMAC, Egain, and Cebyc showcase strong financial development in 2020 with 8% total topline growth with a near fivefoldincrease in EBITDA to a margin of 10%. The group expects multiple sources of synergies going forward.
Impact dimensions

The challenges we face
Buildings account for ca. 40% of Europe’s energy consumption and 36% of Europe’s emissions. 75% of buildings in the EU are energy inefficient.1 In 2050, 95% will still be in use. One third of all produced food is later wasted, making food waste the third largest emission of greenhouse gases.3 Meanwhile, electricity consumption is set to increase in the next 20 years with close to 60% being used in buildings. Today, despite the fast growth of “prop tech”, only a tiny fraction of the 40 million facilities in the world are benefiting from this technology, and already connected buildings suffer from different types of legacy equipment from differing vendors.
- Statistics from the European Commission: https://ec.europa.eu/info/news/focus-energy-efficiency-buildings-2020-feb-17_en#:~:text=Today%2C%20roughly%2075%25%20of%20the,materials%20when%20constructing%20new%20houses. Estimates of European food waste levels, FUSIONS (2012): https://www.eu-fusions.org/phocadownload/Publications/
- Estimates of European food waste levels,
FUSIONS (2012): https://www.eu-fusions.org/
phocadownload/Publications/Estimates%20of%20
European%20food%20waste%20levels.pdf - Swedish Environmental Research Institute (2020). https://www.ivl.se/english/ivl/our-offer/research-projects/circular-flows/refresh---towards-less-food-waste-in-europe.html#:~:text=Around%20100%20million%20tons%20of,every%20year%20within%20the%20EU.&text=Calculations%20show%20that%20food%20waste,impact%20from%20the%20food%20system.
Lakers - Making water work
SDG alignment

-
Total
12% -
Management
8% -
Board
0%

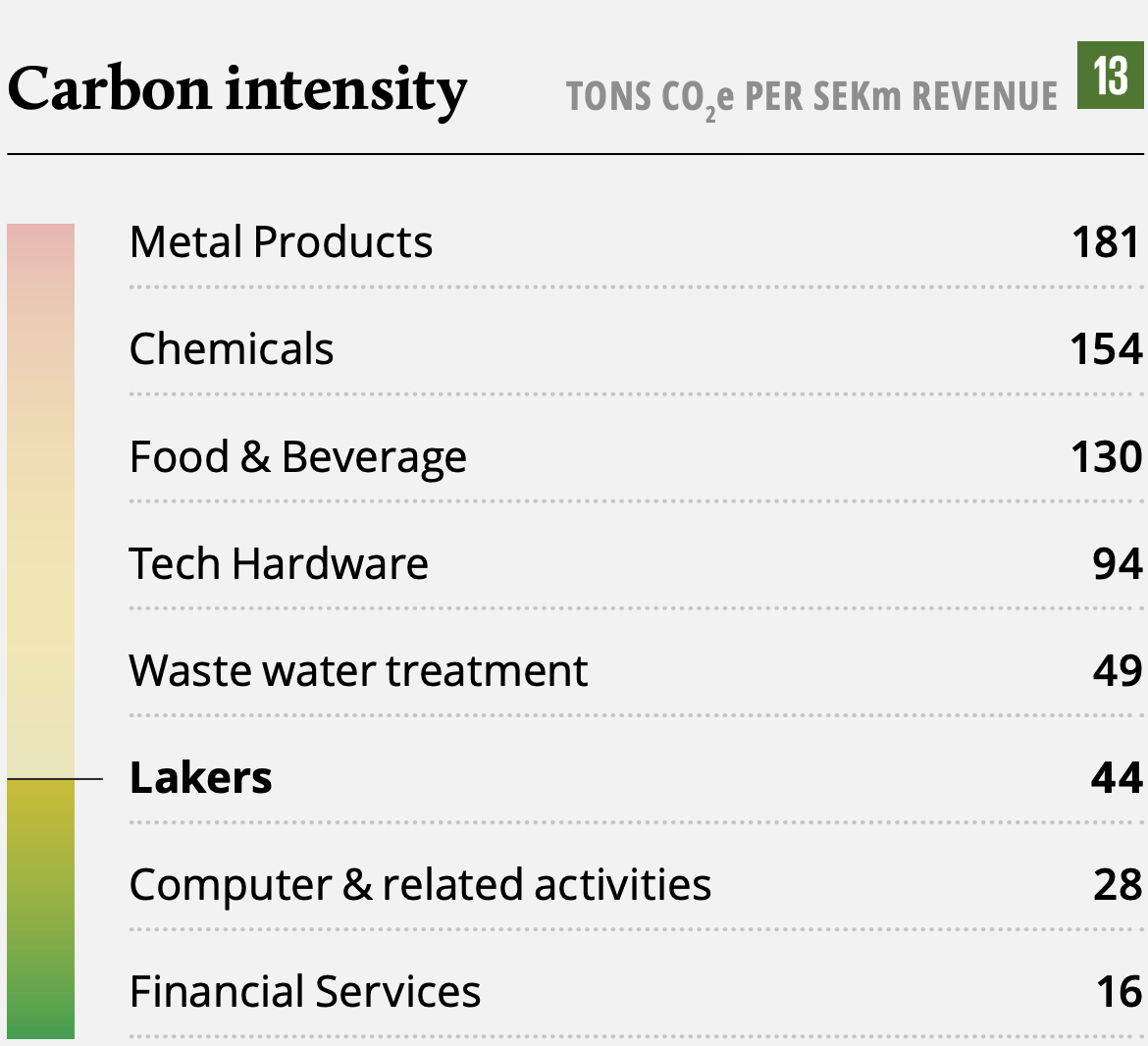
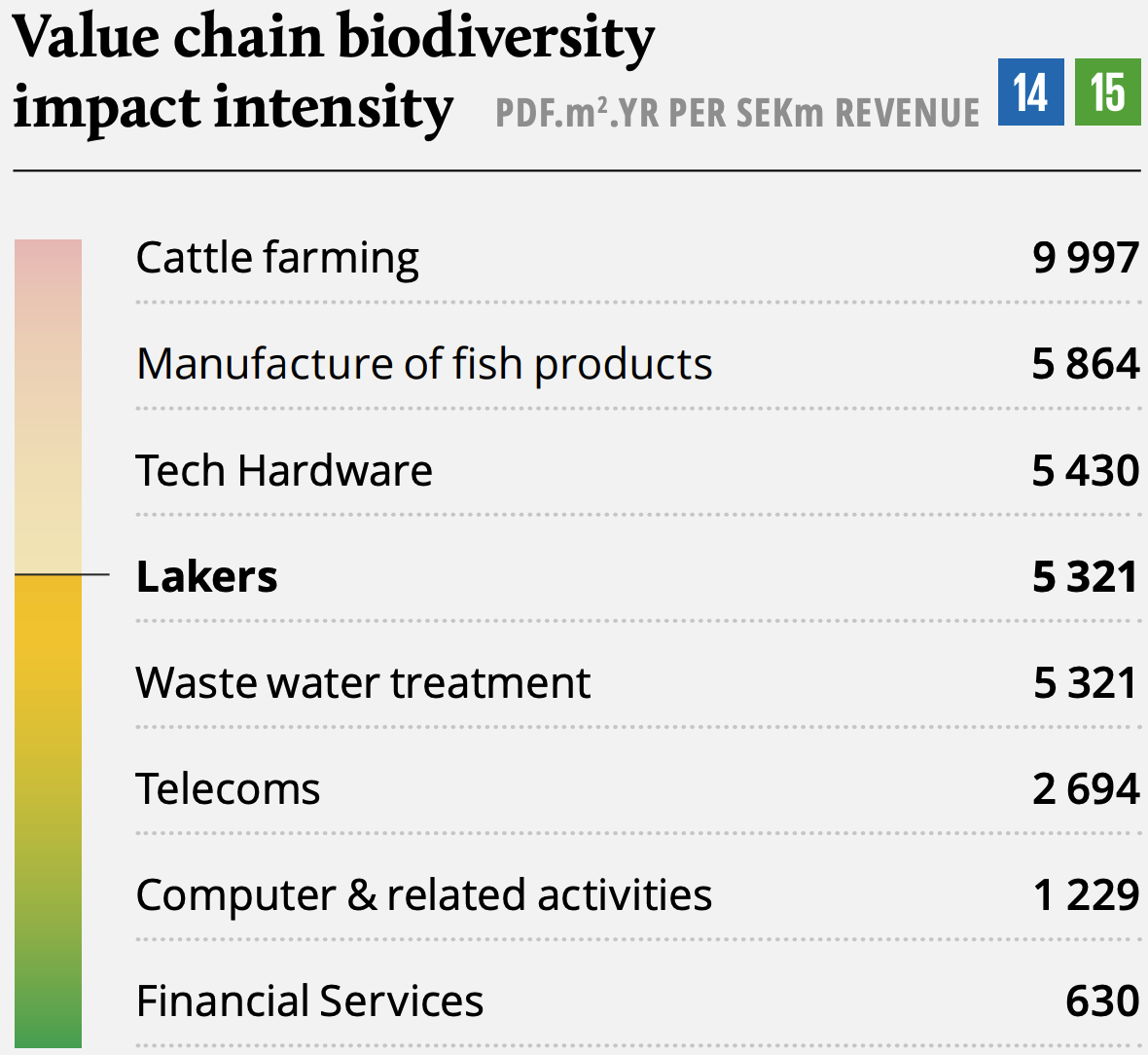
Lakers at a glance
Lakers is a North European aftermarket service provider of maintenance, service, rental, and technical consulting of water pumps, pumping stations, electrical motors, and related components. Water pumps serve as a key component in the infrastructure to transport water. Lakers also offers its customers niche products including pressure vessels, water filters and other related products. Lakers has since Summa’s acquisition in October 2018 grown into a market leader in the Nordics and has recently started its expansion into the UK and Germany, with the ambition to become a leading Northern European player. Today, Lakers operates through 22 entities in Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, the UK, and Germany.
Key developments in 2020
Despite Covid-19, Lakers has performed well during 2020, achieving organic growth of 3%, supported by resilient demand amongst public customers and critical investments in water infrastructure. In 2020, Lakers has worked with a range of initiatives to drive organic value creation and geographic expansion. The company has initiated cross-selling across the group and has further professionalized the platform by strengthening the group function and implementing a new IT system to become more data-driven. Lakers has successfully executed on M&A, acquiring two new companies under 2020, and reached a new milestone by entering Germany. Lakers has continued the strong momentum into 2021, where Lakers reached yet another milestone by entering the UK through the acquisition of Pump Supplies. Lakers has a continued strong pipeline ahead with a focus on expansion in Northern Europe.
- 2018 financials are not pro-forma adj.
Impact dimensions
The challenges we face
The water infrastructure in Northern Europe is aging and underinvested with large inefficiencies. Population growth, urbanization and a changing climate continue to put pressure on water systems. Alongside increasing regulatory standards, this will drive the need for maintenance and upgrades. Pumps account for approximately 10% of the world’s total electricity consumption and about 90% of these works inefficiently. If all pumps were switched to high-efficiency ones, this could save 4% of global electricity consumption1 and reduce yearly water supply loss.
ESG goals
Lakers have recently committed to a set of ESG goals. Among the social targets, they aim to work towards a more equal workforce in their organization. Lakers’ primary climate goal is to decrease their impact on Scope 1 & 2 GHG emissions. Specifically, they aim to increase their share of renewable energy sources (Scope 2) with the long-term ambition for all facilities to use 100% renewable electricity. The goals will be tracked and reported in an annual Sustainability Report.
Norsk Gjenvinning - There is no such thing as waste!

SDG alignment

-
Total
14% -
Management
18% -
Board
43%
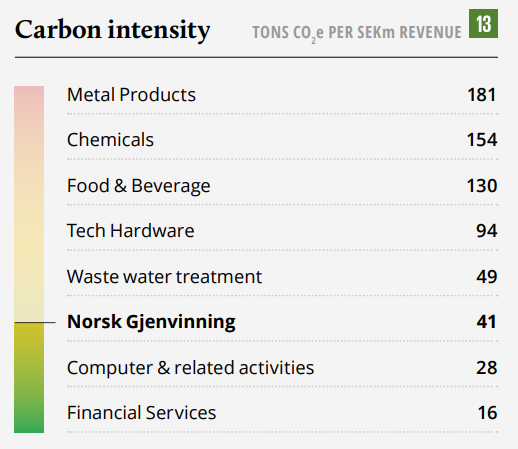
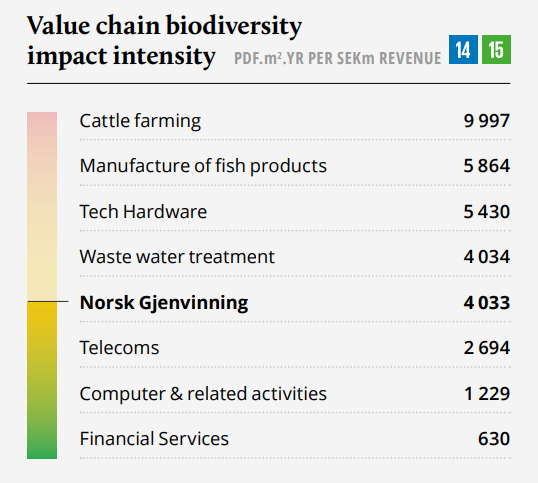
NG at a glance
The Norsk Gjenvinning Group (NG) is Norway’s largest provider of recycling and environmental services, serving more than 40k commercial and municipal customers. The company manages 2.1 million tons of waste per annum, which is close to 20% of all waste in Norway, and additionally has a growing presence in Sweden and Denmark.
Key business areas include commercial waste management (Recycling), metals recycling, household collection, demolition services, industrial services, security shredding, downstream sales, waste trading and depot.
Key developments in 2020
NG experienced a dip in revenues of -1% vs. 2019, due to Covid-19. However, the company delivered positive EBITDA growth during 2020 (26%), demonstrating company resilience and operational flexibility in a tougher macroeconomic environment caused by the pandemic. The Group also continued to deliver on its buy and build strategy, through the acquisition of Saneringsteknikk. During 2020, NG received broad recognition for the important work the company does for the Norwegian society and circular economy, through awards such as «Green Company of the year», «Norwegian Lean company of the year» and «Norway's Smartest Industrial Company».
Impact dimensions

The challenges we face
Global waste generation is expected to grow by 70% by 20501, while the supply of natural resources is scarce. With a rapidly growing population, we have no choice but to recover and reuse materials through a circular economy.
- What a Waste 2.0, World Bank Group, 2018, Available at: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/what-a-waste/trends_in_solid_waste_management.html
- https://www.ssb.no/avfregno
- EPA, 2019. Available at: https://www.epa.gov/energy/greenhouse-gas-equivalencies-calculator
Milarex - Convenient, high quality seafood for all

SDG alignment

-
Total
65% -
Management
39% -
Board
20%
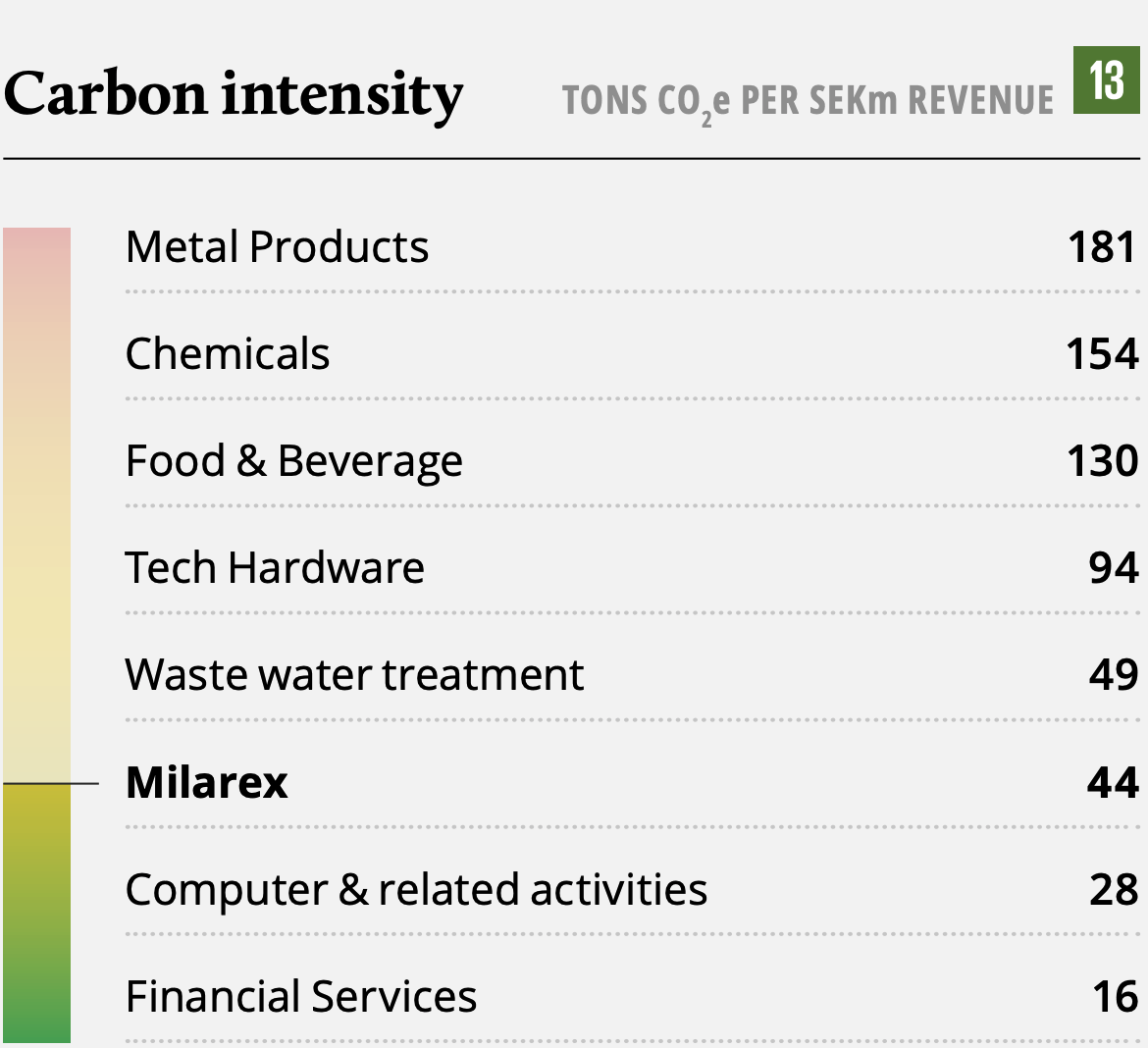
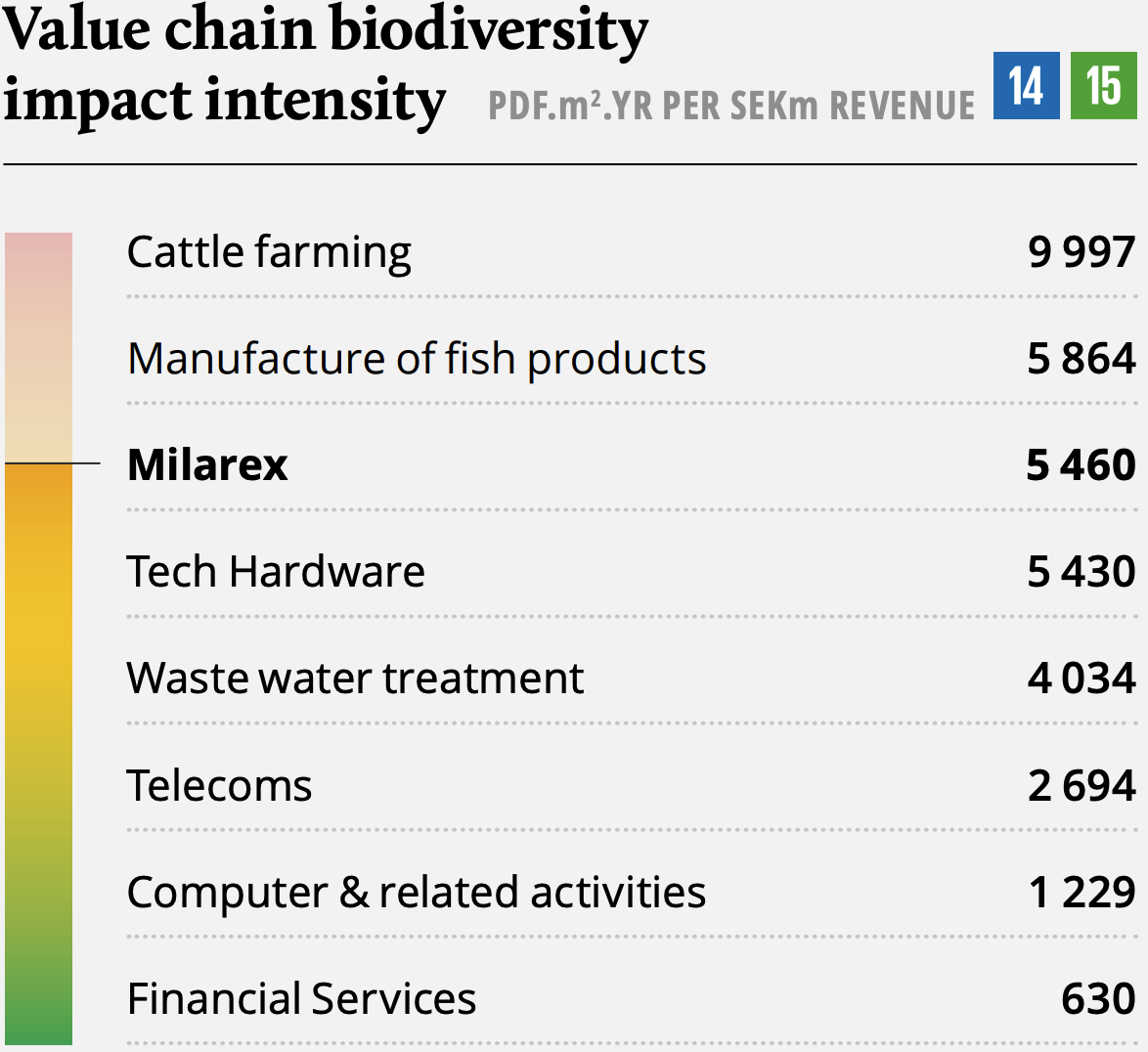
Milarex at a glance
Milarex operates within the secondary processing part of the value chain, focusing on salmon value-added products. The company was established in 2016 and has in a short time taken a leading position within value-added processing of salmon globally, producing 21m kilos of edible products in 2020. The company is headquartered in Norway with manufacturing and other operations in Poland as well as sales and distribution offices across Germany, Italy, UK, and France. In 2021, Milarex expanded to North America through the acquisition of its exclusive distributor, Ultco. Milarex operates one of the world’s most advanced salmon processing factories, which is well invested and has ample room to cater for growth going forward.
Key developments in 2020
Milarex has performed well during 2020, delivering 25% top-line growth supported by strong demand in the retail segment. The company has experienced high growth in markets such as Italy, France, and North America, where Milarex expects continued strong momentum going forward.
Milarex has taken a leadership role in sustainable practices in the salmon processing industry. They have set ambitious targets and have in 2020launched a fish traceability platform, introduced fully recyclable plastics in its consumer brand Arctic Fish, and launched a sustainable best practice product ‘Pure Green’ under the same brand.
With the recent acquisition of the US distributor Ultco, Milarex is well positioned to further ramp up its efforts in North America, representing a new growth chapter for the company.
- Several additional SDGs are part of Milarex' strategic considerations and diligent work on sustainability. We here seek to highlight a few core positive contributions directly related to Milarex operations. It is an integral part of Milarex' strategy be best-inclass on acting to avoid harm to marine ecosystems through sourcing sustainable raw materials. Milarex seeks to challenge suppliers and peers to move the industry forward in terms of sustainability.
Impact dimensions

The challenges we face¹
The world population is estimated to reach 8.6 billion people by 2030, implying a demand for 35% more food than what we have available today. On a global basis, more than 1.9 million adults are classified as overweight2, representing a need for a healthier diet to combat the disease. Also, of the total GHG emissions that we have today, approximately 14.5% is due to livestock3. These challenges represent opportunities for healthy protein producers, such as Milarex, to step up by increasing volume and improving the efficiency of food production.
- Future of Food. https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/474831468186561685/future-of-food-shaping-the-global-food-system-to-deliver-improved-nutrition-and-health
- WHO, 2018. Obesity and overweight. http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
- FAO, 2013. Tackling Climate Change Through Livestock. http://www.fao.org/3/i3437e/i3437e.pdf
- FAO, Key facts and findings: http://www.fao.org/news/story/en/item/197623/icode/
- SINTEF, 2009. Carbon footprint and energy consumption of Norwegian seafood products. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/301694542_Carbon_footprint_and_energy_use_of_Norwegian_seafood_products_-_Final_report_2009
- Substituting seafood for red meat is thought to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease for example, which maps to SDG subgoal indicator 3.4.1.











